It’s a hereditary coagulation disorder due to deficiency of coagulation factors result in hemorrhagic tendency.
Serious complications can result from bleeding into the joints, muscles, brain, or other internal organs.
In severe cases recurrent hemorrhage in joint space is common causing Hemophiliac arthropathy
• Joint pain, fever, joint swelling
• Ankle is involved in children, knee joint in adult
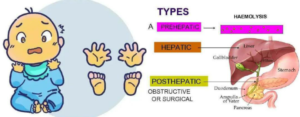
TYPES
1. Haemophilic A = Factor 8
2. Haemophilic B = Factor 9
CAUSES
Hemophilia occurs when a clotting factor is missing or levels of clotting factors are low.
Coagulation factors are proteins in the blood that help control bleeding. When injury occurs that causes bleeding, that time coagulation factors work together to form a blood clot. The clot stop too much blood loose.
SYMPTOMS
• Manifested in infant
• Males are mainly affected
• Positive family history
• Bleeding usually follows after trauma
• Characteristic of bleeding is not due to it’s profuseness, but persistent over days Or weeks
• Spontaneous hemorrhage is rare
• Hemorrhage mainly from nose, urinary track, muscle, joint, subcutaneous tissue
• Cutaneous hemorrhage is rare
• In severe cases recurrent hemorrhage in joint space is common causing Haemophilic arthropathy
• Sometimes hemorrhage in muscle, may lead to pain fever and swelling.
COMPLICATION
1. Haemophilic arthropathy
2. Blood transfusion hazards
INVESTIGATION
1. Blood Routine examination
HB% Low
BT normal, CT prolong
Factors Vlll is diminished
2. X-Ray – Tumor like masses called haemophilic pseudo tumour in the bone present sue to subcutaneous haemorrhage
TREATMENT