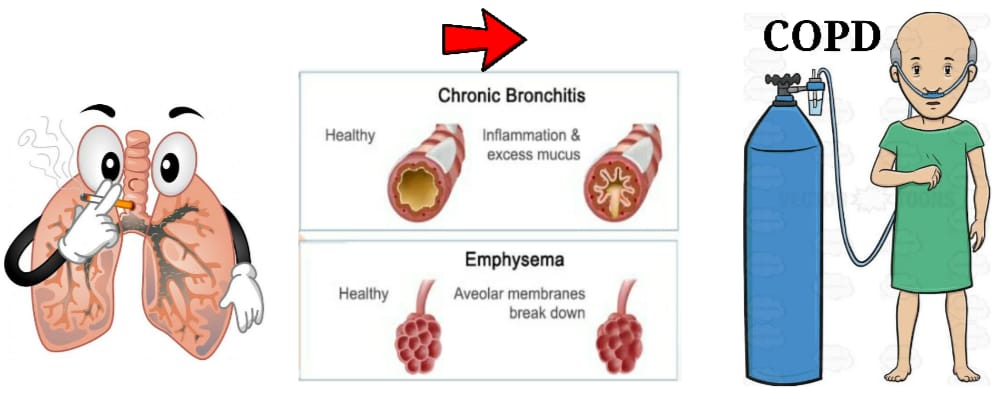
COPD Or Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a group of progressive and persistent lung disease named as EMPHYSEMA, CHRONIC BRONCHITIS and small airway disease such as bronchiolytis
Emphysema– abnormal persistent enlargement of the airspace distal to the terminal bronchioles accompanied by destruction of there walls and without obvious fibrosis
Chronic bronchitis- persistent productive cough for atleast 3 Consiqutive months in each of 2 consicutive years
Untreated, COPD can lead to a faster progression of the disease
CAUSATION
1.most of the people suffering from this disease are atleast 40 years old and having history of smoking
2.Occupational exposure such as coal dust, silica and cadmium
3.Genetic factors- alfa 1 antitrypsin deficiency
4.Indor air pollution like cooking with biomass in undevoloping countries
5.Lo socio economic status
CLINICAL TYPES
Blue bloters- that means COPD with predominantly chronic bronchitis
Features-
1.severe hypoxia
2.Hypercapnia refers to increased CO2 in blood
3.pulmonary hypertension
4.Central cynosis(blue)
5.Right ventricular failure
6.Oedema(bloter)
Pink puffers- that means COPD with predominant emphysema
Features-
1.ventrilatory capillary impaired
2.Less cyanosis
3.per’s lip breathing or puffying to blow up the CO2(high inter Alveolar pressure)
SIGN AND SYMPTOMS
1.Breadthless ness
2.Frequent coughing or wheezing
3.Trouble taking a deep breath
4.Excess phlegm, mucus, or sputum
5.Chest tightness
6.lack of energy
7.weight loss
Swelling in ankles, feet or legs
INVESTIGATION
Commonly COPD is remain misdiagnosed until the advance stage.
To diagnose the disease your doctor may ask you for sign & symptoms, history and lifestyle.
Tests-
1.Pulmonary Function Text
2.Chest X-ray-
3.CT scan-
4.Arterial blood gas analysis(ABG) –
Privative–
Quitting smoking
Medication- short acting bronchodialator include
1.Albuterol
2.Ipratropium
3.Levalbuterol
Long acting include
1.Acidinum
2.Arfomoterol
3.Indacaterol
4.Tiotropium
5.Salmeterol
6.Umeclidinum
Inhaled Steroids
1.Fluticasone
2.Budesonide